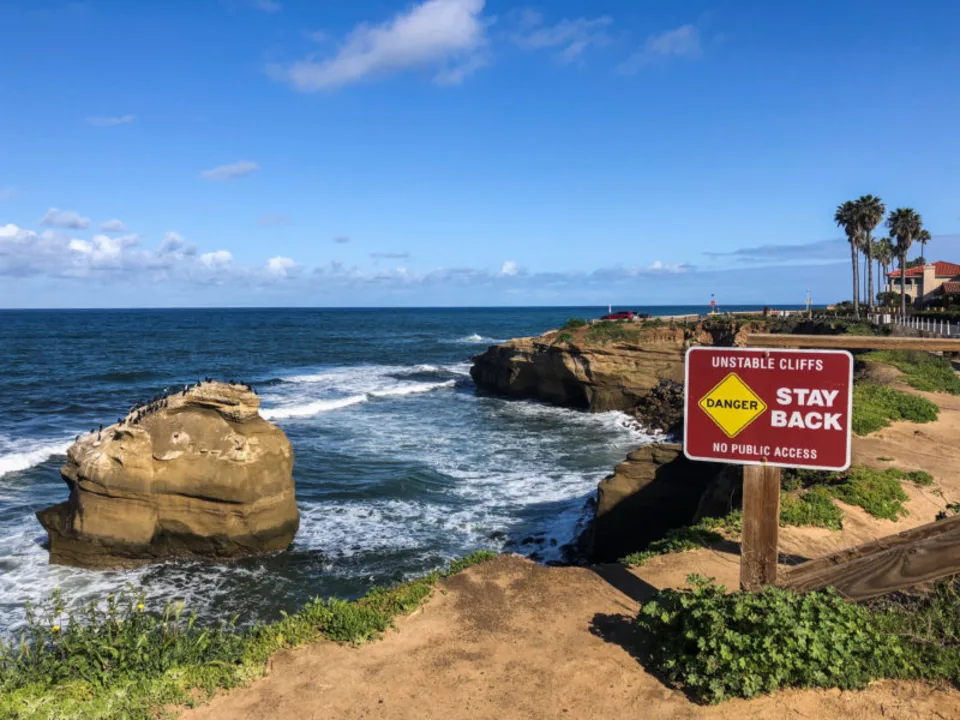
Why has the sea level not risen in some areas?
Investigating the Causes of Sea Level Stability in Certain Areas
The sea level is a global phenomenon, however, in some areas, it has remained remarkably stable throughout the years. This has confused many researchers, as the majority of the world's oceans have been experiencing increases in sea level, due to a variety of factors such as global warming and melting ice sheets. To understand why the sea level has not risen in certain areas, it is important to investigate the various causes of this stability.
Shift in Wind Patterns
The primary cause of sea level stability in certain areas is a shift in wind patterns. Wind carries water from one area to another, and when the wind patterns shift, the water is moved away from some areas and towards others. This can cause sea levels in certain areas to remain stable, even as sea levels increase in other areas.
Ocean Currents
Another factor that can cause sea level stability in certain areas is ocean currents. Ocean currents are powerful forces of nature, and they can have a significant impact on the sea level in certain areas. For example, in some areas, ocean currents can carry cold water from the Arctic Ocean and push it towards the equator. This can lead to a decrease in the sea level in certain areas, even as the sea level is rising in other areas.
Tectonic Activity
Tectonic activity can also play a role in sea level stability in certain areas. The Earth's crust is made up of individual plates that move around, and when these plates move, they can cause the land in certain areas to rise or sink. This is known as land subsidence, and it can cause sea levels in certain areas to remain stable, even as sea levels are rising in other areas.
Human Activity
Finally, human activity can also play a role in sea level stability in certain areas. For example, in some areas, humans have built dams and other structures that can affect the flow of water and prevent sea levels from rising. In other areas, humans have been extracting groundwater, which can lead to a decrease in sea levels.
In conclusion, when investigating the causes of sea level stability in certain areas, it is important to consider both natural and human factors. Wind patterns, ocean currents, tectonic activity, and human activity can all play a role in keeping sea levels stable in certain areas, even as sea levels are rising in other areas.
Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Sea Level Stability
Climate change is a major factor in sea level stability. Warmer temperatures cause melting of polar icecaps, which adds to the sea level. Sea levels are rising across the globe, but the rate of rise may vary depending on the location.
The rate of sea level rise is determined by a variety of factors, including regional oceanographic and atmospheric conditions. The regional oceanographic conditions may include wind patterns, ocean currents, and local bathymetry. Atmospheric conditions such as air temperature, humidity, and pressure also play a role. These factors can interact to create areas of sea level stability or instability.
In some areas, sea level rise may be slowed or even halted due to natural processes such as coastal upwelling. Upwelling is a process in which cold, nutrient-rich water rises from the ocean depths to the surface. This process is driven by wind patterns, and can cause a decrease in sea level near the coasts.
In addition, regional oceanographic and atmospheric conditions can have a direct impact on the rate of sea level rise. For example, a decrease in the salinity of the ocean due to increased precipitation can slow sea level rise. This can be especially true in areas where there is a high rate of evaporation, such as in the tropics.
Climate change can also affect sea level stability in other ways. Changes in the global climate can lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of storms. These storms can cause disruptions in the ocean circulation patterns, which can then lead to an increase in sea level rise. Additionally, changes in ocean circulation patterns can lead to a decrease in the upwelling process, resulting in an increase in sea level rise.
Climate change can also lead to an increase in air and ocean temperatures, which can also cause an increase in sea level rise. Warmer air holds more water vapor, which can lead to an increase in precipitation and sea level rise. Warmer ocean temperatures can also cause an increase in the rate of evaporation, resulting in an increase in sea level rise.
The effects of climate change on sea level stability are complex and varied. Changes in regional oceanographic and atmospheric conditions, changes in the global climate, and changes in the intensity and frequency of storms all play a role in determining the rate of sea level rise. It is important to understand these factors in order to accurately predict and prepare for the impacts of climate change on sea level rise.
Examining the Effects of Ocean Currents on Sea Level Variation
The ocean is a powerful force that is rapidly changing due to the effects of climate change. As the world's climate continues to warm, the ocean is absorbing more heat and affecting sea levels around the world. However, while sea levels are rising at an alarming rate in some areas, other areas may experience little to no change. This is due to the effects of ocean currents.
Ocean currents refer to the large-scale movement of ocean water in a specific direction. These currents are affected by a variety of factors, such as wind, salinity, and temperature, and can affect the local sea levels in a particular region. For example, if a current is pushing the water up in one region, then the sea level in that area may not rise as much as in other areas. On the other hand, if a current is pushing the water down in another region, then the sea level in that area may rise significantly more than in other areas.
In addition to affecting local sea levels, ocean currents also play an important role in the global climate. Warm ocean currents can transport heat from the equator to the poles, while cold ocean currents can transport cold from the poles to the equator. This helps to regulate the global temperature and can affect the climate in far-reaching ways. For example, the Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that brings warm air to Europe, making it a much milder climate than other regions at the same latitude.
The effects of ocean currents, therefore, can be seen in the variation of sea levels in different areas. While some areas may experience a dramatic rise in sea level due to the effects of climate change, other areas may remain relatively unchanged. This is because the ocean currents in those areas may be pushing the water in a different direction, thus preventing the local sea level from rising as much as in other areas. Therefore, it is important to consider the effects of ocean currents when looking at sea level variations around the world.
Analyzing the Role of Sea Floor Topography in Sea Level Stability
Sea level is one of the most important environmental indicators, and its stability is essential for the health of our planet. While it is widely understood that climate change and human activity have caused sea levels to rise in many areas, it is less well known that in some areas sea levels have not risen.
To understand why sea levels have not risen in some areas, it is important to analyze the role of sea floor topography. Sea floor topography is the shape and structure of the ocean floor. It can range from flat plains to deep trenches and steep slopes. The shape of the sea floor is the main factor that determines whether sea levels rise or fall in an area.
In areas with a flat sea floor, such as the Florida Keys, the tides and waves will cause a steady rise in sea level. This is because the flat sea floor is unable to absorb the energy of the waves and tides, causing the water to pile up in the area. On the other hand, in areas with deep trenches and steep slopes, such as the deep ocean trenches in the Pacific Ocean, the sea floor is able to absorb the energy of the waves and tides, causing the water to move away from the area and preventing a rise in sea level.
The role of sea floor topography in sea level stability is further complicated by the presence of deep sea currents. Deep sea currents are created when the water on the surface is heated by the sun, causing it to rise and move away from the area. This causes a flow of cooler, deeper water to move into the area in its place. This deep water is denser than the surface water and is able to absorb more energy from the tides and waves, further preventing a rise in sea level.
In addition to sea floor topography and deep sea currents, other factors such as wind, atmospheric pressure, and ocean salinity can also affect sea level stability. Wind can cause the water to pile up in certain areas, while atmospheric pressure can cause the water to be pushed away from the area. Ocean salinity can also affect sea level stability as saltier water is denser and therefore more likely to absorb the energy of the waves and tides.
In conclusion, sea floor topography, deep sea currents, wind, atmospheric pressure, and ocean salinity all play an important role in determining whether sea levels will rise or fall in an area. By understanding these factors, we can better understand why sea levels have not risen in some areas.
Exploring the Interplay of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise in Different Locations
As global temperatures rise, it may seem logical for the sea level to follow suit. But the reality is that sea levels have not risen in some areas, which has raised questions about the impact of global warming on sea levels in different parts of the world. To better understand the complex interplay between global warming and sea level rise, it is important to examine the many factors that influence water levels in different locations.
Natural Climate Cycles
The world’s climate is constantly changing, and the same can be said for the ocean. Natural cycles such as El Niño and La Niña can have a significant impact on sea levels in certain regions. El Niño, for example, is a phenomenon characterized by the warming of ocean surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, which can cause sea levels to drop in some areas. Similarly, La Niña, which is characterized by cooler ocean temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, can lead to higher sea levels in certain regions.
Ocean Currents
In addition to natural cycles, ocean currents can also affect sea levels in different parts of the world. For example, the Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current that runs from the Gulf of Mexico to the North Atlantic Ocean. This current can have a significant impact on sea levels in the North Atlantic, as it is responsible for transporting warm water from the south to the north. This can lead to higher sea levels in the North Atlantic, while the opposite is true for the South Atlantic.
Local Weather Patterns
Local weather patterns can also have an impact on sea levels in certain areas. For example, areas with strong winds can cause sea levels to rise, while areas with high pressure can cause sea levels to drop. This is because wind and atmospheric pressure both affect the amount of water that is evaporating from the ocean, which can lead to higher or lower sea levels in certain parts of the world.
Ice Melting
Another factor that can affect sea levels is the melting of ice. As global temperatures rise, the world’s glaciers and ice sheets are melting at an unprecedented rate. This can lead to higher sea levels in certain regions, as the melting ice adds more water to the ocean. Sea levels are also affected by the melting of ice in the form of icebergs, which can break off from glaciers and drift away, adding more water to the ocean.
Conclusion
Understanding the complex interplay between global warming and sea level rise is essential for predicting and responding to global climate change. The many factors that influence sea levels in different locations make it difficult to predict how individual regions will be impacted by global warming. However, by examining the natural climate cycles, ocean currents, local weather patterns, and melting ice, we can gain a clearer understanding of how sea levels may change in the future.